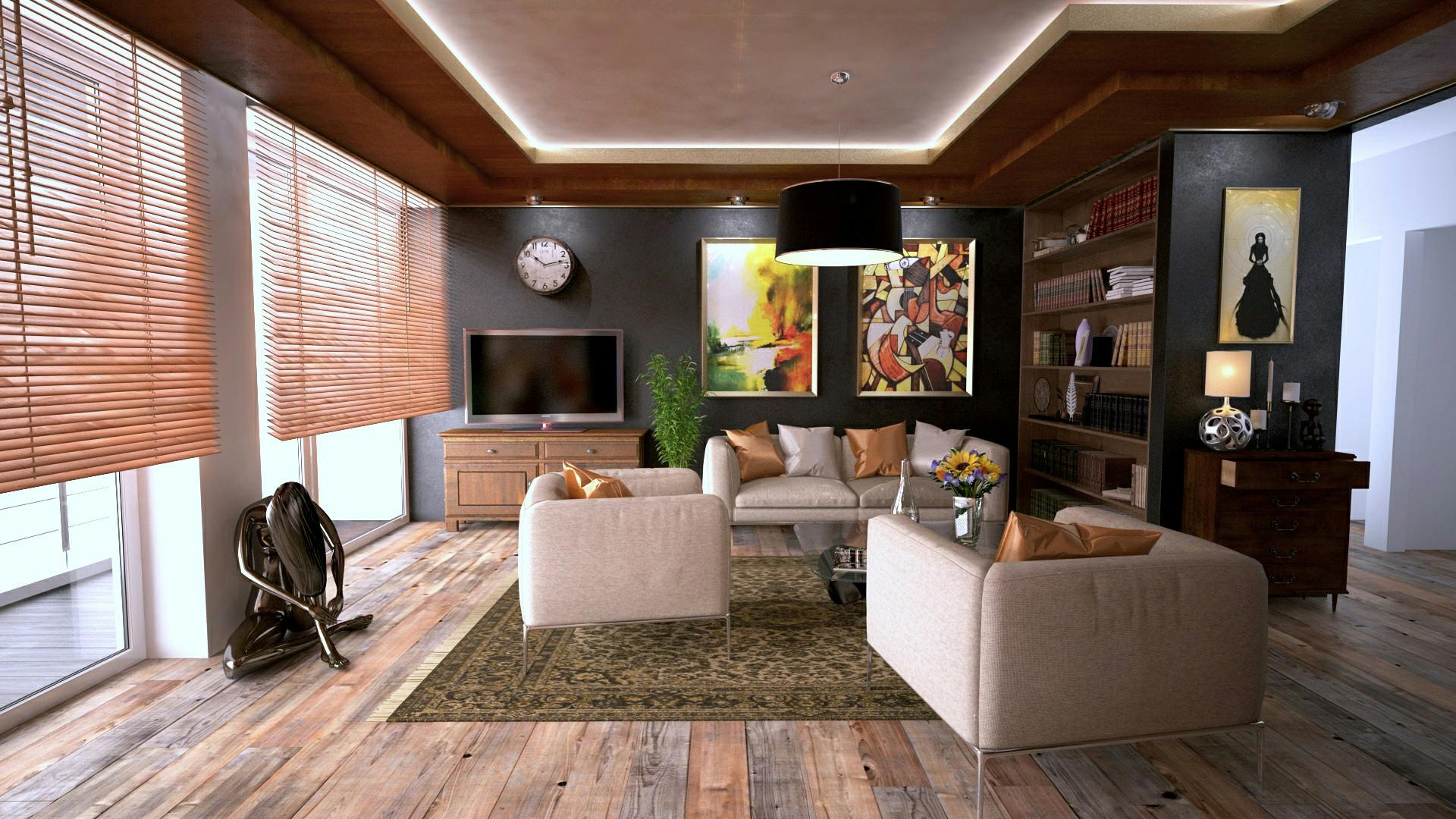
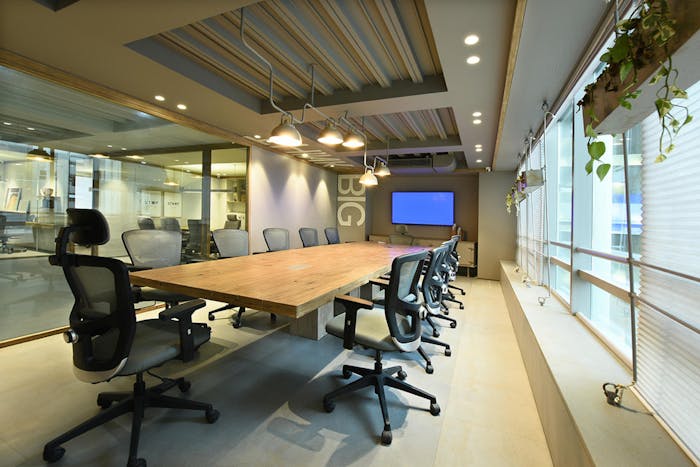
What is False Ceiling ?
False Ceiling A false ceiling, also known as a dropped ceiling or suspended ceiling, is a secondary ceiling installed below the main structural ceiling. It is typically made from materials like gypsum, PVC, wood, or metal and is supported by a metal framework. False ceilings are used to enhance aesthetics, improve acoustics, provide insulation, and conceal wiring, ducts, and other structural elements. They come in various designs, including grid patterns, coffered ceilings, and decorative panels, making them a popular choice for modern interiors. Apart from enhancing visual appeal, false ceilings also help regulate room temperature and improve energy efficiency by reducing the overall ceiling height, thus optimizing the use of air conditioning and lighting systems.